- Linux Boot Process
- Linux Partition
- Linux File System Hierarchy
- Important Configuration files Linux
- /Proc
- Server configuration file s and Packages
- Monitoring Commands
- Port Numbers In Linux
9.Linux Logs
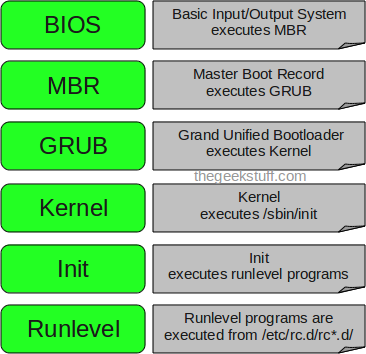
Linux Boot Process (Startup Sequence)
Linux Partition for OS installation
/
/boot
Swap
/home
/var
/etc
Linux Directory Structure/ File System
Linux Server and Port number
20 – FTP Data (For transferring FTP data)
21 – FTP Control (For starting FTP connection)
22 – SSH(For secure remote administration which uses SSL to encrypt the transmission)
23 – Telnet (For insecure remote administration
25 – SMTP(Mail Transfer Agent for e-mail server such as SEND mail)
53 – DNS(Special service which uses both TCP and UDP)
68 – DHCP
69 – TFTP(Trivial file transfer protocol uses udp protocol for connection less transmission of data)
80 – HTTP/WWW (apache)
88 – Kerberos
110 – POP3(Mail delivery Agent)
123 – NTP(Network time protocol used for time syncing uses UDP protocol)
137 – NetBIOS(nmbd)
139 – SMB-Samba(smbd)
143 – IMAP
995 – POP3s
161 – SNMP(For network monitoring)
389 – LDAP(For centralized administration)
443 – HTTPS(HTTP+SSL for secure web access)
636 – ldaps(both tcp and udp)
873 – rsync
989 – FTPS-data
990 – FTPS
993 – IMAPS
2049 – NFS(nfsd, rpc.nfsd, rpc, portmap) 2401 – CVS server
3306 – MySql
1. /proc Directories with names as numbers
Do a ls -l /proc, and you’ll see lot of directories with just numbers. These numbers represents the process ids, the files inside this numbered directory corresponds to the process with that particular PID.
Following are the important files located under each numbered directory (for each process):
- cmdline – command line of the command.
- environ – environment variables.
- fd – Contains the file descriptors which is linked to the appropriate files.
- limits – Contains the information about the specific limits to the process.
- mounts – mount related information
Following are the important links under each numbered directory (for each process):
- cwd – Link to current working directory of the process.
- exe – Link to executable of the process.
- root – Link to the root directory of the process.
2. /proc Files about the system information
Following are some files which are available under /proc, that contains system information such as cpuinfo, meminfo, loadavg.
/proc/cpuinfo – information about CPU,
- /proc/meminfo – information about memory,
- /proc/loadvg – load average,
- /proc/partitions – partition related information,
- /proc/version – linux version
Some Linux commands read the information from this /proc files and displays it. For example, free command, reads the memory information from /proc/meminfo file, formats it, and displays it.
To learn more about the individual /proc files, do “man 5 FILENAME”.
- /proc/cmdline – Kernel command line
- /proc/cpuinfo – Information about the processors.
- /proc/devices – List of device drivers configured into the currently running kernel.
- /proc/dma – Shows which DMA channels are being used at the moment.
- /proc/fb – Frame Buffer devices.
- /proc/filesystems – File systems supported by the kernel.
- /proc/interrupts – Number of interrupts per IRQ on architecture.
- /proc/iomem – This file shows the current map of the system’s memory for its various devices
- /proc/ioports – provides a list of currently registered port regions used for input or output communication with a device
- /proc/loadavg – Contains load average of the system
The first three columns measure CPU utilization of the last 1, 5, and 10 minute periods.
The fourth column shows the number of currently running processes and the total number of processes.
The last column displays the last process ID used. - /proc/locks – Displays the files currently locked by the kernel
Sample line:
1: POSIX ADVISORY WRITE 14375 08:03:114727 0 EOF - /proc/meminfo – Current utilization of primary memory on the system
- /proc/misc – This file lists miscellaneous drivers registered on the miscellaneous major device, which is number 10
- /proc/modules – Displays a list of all modules that have been loaded by the system
- /proc/mounts – This file provides a quick list of all mounts in use by the system
- /proc/partitions – Very detailed information on the various partitions currently available to the system
- /proc/pci – Full listing of every PCI device on your system
- /proc/stat – Keeps track of a variety of different statistics about the system since it was last restarted
- /proc/swap – Measures swap space and its utilization
- /proc/uptime – Contains information about uptime of the system
- /proc/version – Version of the Linux kernel, gcc, name of the Linux flavor installed.
Linux Log Files
- /var/log/messages – Contains global system messages, including the messages that are logged during system startup. There are several things that are logged in /var/log/messages including mail, cron, daemon, kern, auth, etc.
- /var/log/dmesg – Contains kernel ring buffer information. When the system boots up, it prints number of messages on the screen that displays information about the hardware devices that the kernel detects during boot process. These messages are available in kernel ring buffer and whenever the new message comes the old message gets overwritten. You can also view the content of this file using the dmesg command.
- /var/log/auth.log – Contains system authorization information, including user logins and authentication machinsm that were used.
- /var/log/boot.log – Contains information that are logged when the system boots
- /var/log/daemon.log – Contains information logged by the various background daemons that runs on the system
- /var/log/dpkg.log – Contains information that are logged when a package is installed or removed using dpkg command
- /var/log/kern.log – Contains information logged by the kernel. Helpful for you to troubleshoot a custom-built kernel.
- /var/log/lastlog – Displays the recent login information for all the users. This is not an ascii file. You should use lastlog command to view the content of this file.
- /var/log/maillog /var/log/mail.log – Contains the log information from the mail server that is running on the system. For example, sendmail logs information about all the sent items to this file
- /var/log/user.log – Contains information about all user level logs
- /var/log/Xorg.x.log – Log messages from the X
- /var/log/alternatives.log – Information by the update-alternatives are logged into this log file. On Ubuntu, update-alternatives maintains symbolic links determining default commands.
- /var/log/btmp – This file contains information about failed login attemps. Use the last command to view the btmp file. For example, “last -f /var/log/btmp | more”
- /var/log/cups – All printer and printing related log messages
- /var/log/anaconda.log – When you install Linux, all installation related messages are stored in this log file
- /var/log/yum.log – Contains information that are logged when a package is installed using yum
- /var/log/cron – Whenever cron daemon (or anacron) starts a cron job, it logs the information about the cron job in this file
- /var/log/secure – Contains information related to authentication and authorization privileges. For example, sshd logs all the messages here, including unsuccessful login
/var/log/wtmp or /var/log/utmp – Contains login records. Using wtmp you can find out who is logged into the system. who command uses this file to display the information.
- /var/log/faillog – Contains user failed login attemps. Use faillog command to display the content of this file.
Apart from the above log files, /var/log directory may also contain the following sub-directories depending on the application that is running on your system.
- /var/log/httpd/ (or) /var/log/apache2 – Contains the apache web server access_log and error_log
- /var/log/lighttpd/ – Contains light HTTPD access_log and error_log
- /var/log/conman/ – Log files for ConMan client. conman connects remote consoles that are managed by conmand daemon.
- /var/log/mail/ – This subdirectory contains additional logs from your mail server. For example, sendmail stores the collected mail statistics in /var/log/mail/statistics file
- /var/log/prelink/ – prelink program modifies shared libraries and linked binaries to speed up the startup process. /var/log/prelink/prelink.log contains the information about the .so file that was modified by the prelink.
- /var/log/audit/ – Contains logs information stored by the Linux audit daemon (auditd).
- /var/log/setroubleshoot/ – SELinux uses setroubleshootd (SE Trouble Shoot Daemon) to notify about issues in the security context of files, and logs those information in this log file.
- /var/log/samba/ – Contains log information stored by samba, which is used to connect Windows to Linux.
- /var/log/sa/ – Contains the daily sar files that are collected by the sysstat package.
- /var/log/sssd/ – Use by system security services daemon that manage access to remote directories and authentication mechanisms.